how many phosphate groups in dna Dna strand nucleotides end addition macmillanhighered each grows its
Recently, I came across some fascinating information that delves into the intricate world of DNA. As professionals in the field, it is crucial for us to constantly stay updated with the latest advancements and discoveries, and this new piece of knowledge certainly piqued my interest.
SOLVED: Suppose Two Phosphate Groups in DNA
 One of the images I found showcases the structure of DNA with a focus on its phosphate groups. In DNA, there are two phosphate groups, each with a charge of -1.
One of the images I found showcases the structure of DNA with a focus on its phosphate groups. In DNA, there are two phosphate groups, each with a charge of -1.
Understanding the functions and properties of phosphate groups is essential for comprehending the way DNA is structured and works. These phosphate groups, along with the sugar molecules and nitrogenous bases, form the backbone of the DNA double helix. The negatively charged phosphate groups help stabilize the structure by attracting and bonding with the positively charged histone proteins. This interaction plays a significant role in DNA packaging and organization within the nucleus.
Furthermore, the negatively charged phosphate groups repel each other, which contributes to the stability of the DNA double helix. This electrostatic repulsion prevents the strands from collapsing onto each other and ensures that DNA remains in its characteristic twisted ladder shape.
However, it’s important to note that the phosphate groups alone do not dictate DNA’s hereditary information. Instead, it is the sequence of the nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) that forms the genetic code encoded within DNA.
The Structure of DNA: Concepts of Biology
 The second image I encountered provides an overview of the structure of DNA. This image depicts the double helix structure, with the nitrogenous bases connected in the middle like rungs of a ladder.
The second image I encountered provides an overview of the structure of DNA. This image depicts the double helix structure, with the nitrogenous bases connected in the middle like rungs of a ladder.
As we all know, DNA carries the genetic information necessary for the development and functioning of all living organisms. It does this through the specific pairing of the nitrogenous bases: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C). This complementary base pairing follows specific rules, specifically, Adenine forming hydrogen bonds with Thymine (A-T) and Guanine with Cytosine (G-C).
This precise base pairing is crucial during DNA replication and protein synthesis. When DNA is replicated, the two strands separate, and each serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This complementary base pairing ensures that the genetic information is accurately preserved and transferred to the newly formed DNA strands.
Moreover, the double helix structure allows DNA to be compactly packaged within the cell nucleus while remaining easily accessible for cellular processes such as transcription and translation. This efficient packaging is facilitated by chromatin, which is formed by DNA wrapping around histone proteins and further coiling and folding.
These images and the associated information provide a glimpse into the fascinating world of DNA. As professionals, it is crucial for us to delve into such intricacies to stay updated and enhance our knowledge. Understanding the structure and functions of DNA is foundational to countless fields, including genetics, molecular biology, and even medical research.
By constantly expanding our knowledge of DNA, we can unlock new avenues of research and contribute to scientific advancements that impact various aspects of our lives. Let’s continue to explore and unravel the mysteries of DNA, and discover the numerous possibilities that lie within its complex structure.
If you are looking for Figure 9.7 you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Figure 9.7 like A DNA molecule has many phosphate groups, as shown below What type of, DNA III | Biology | Visionlearning and also Figure 9.7. Here you go:
Figure 9.7
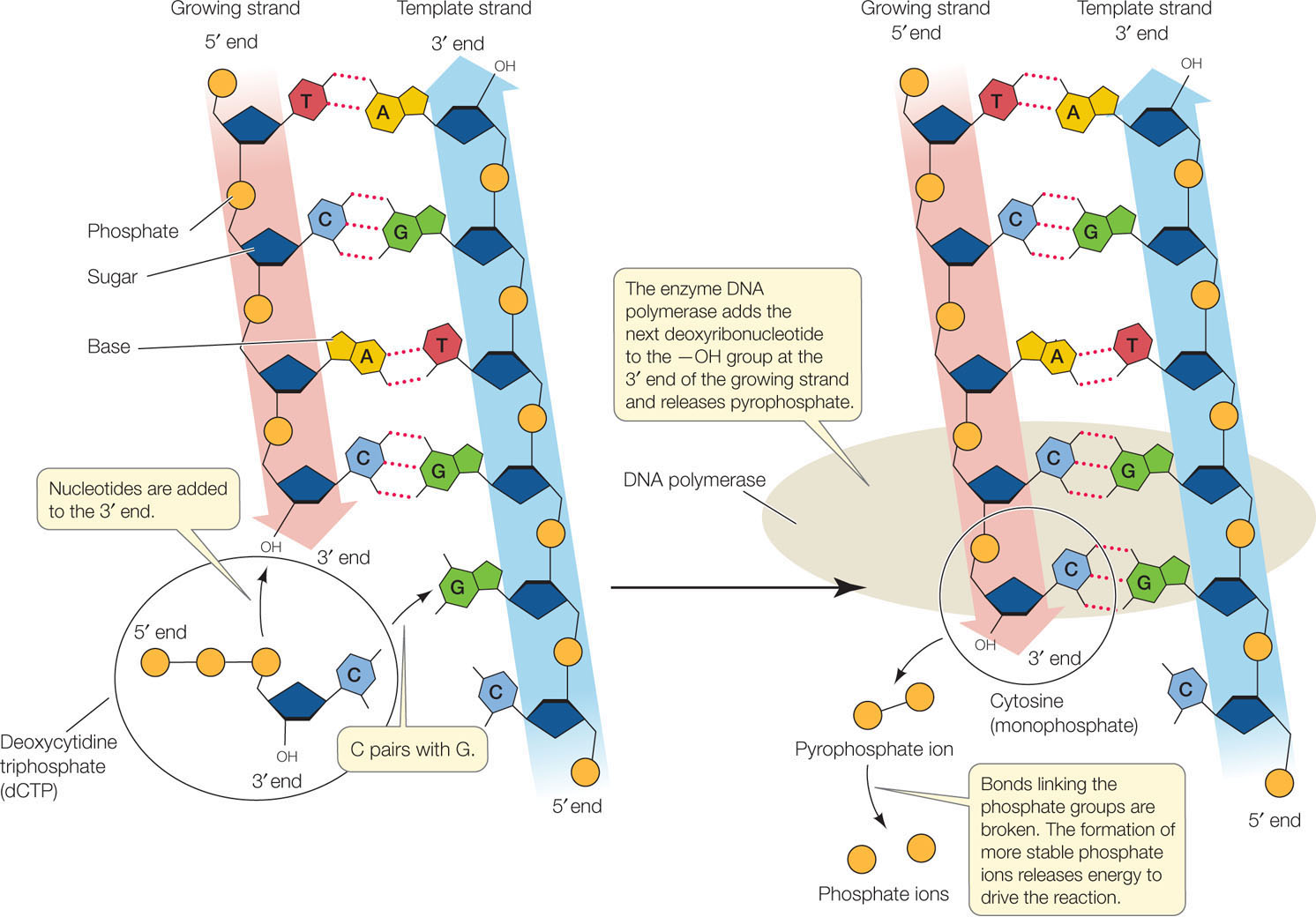 www.macmillanhighered.comdna strand nucleotides end addition macmillanhighered each grows its
www.macmillanhighered.comdna strand nucleotides end addition macmillanhighered each grows its
The Structure Of DNA · Concepts Of Biology
 philschatz.comdna structure base pairs biology adenine thymine double guanine figure helix cytosine ladder stranded rungs made bonds rna forms nucleotides
philschatz.comdna structure base pairs biology adenine thymine double guanine figure helix cytosine ladder stranded rungs made bonds rna forms nucleotides
DNA III | Biology | Visionlearning
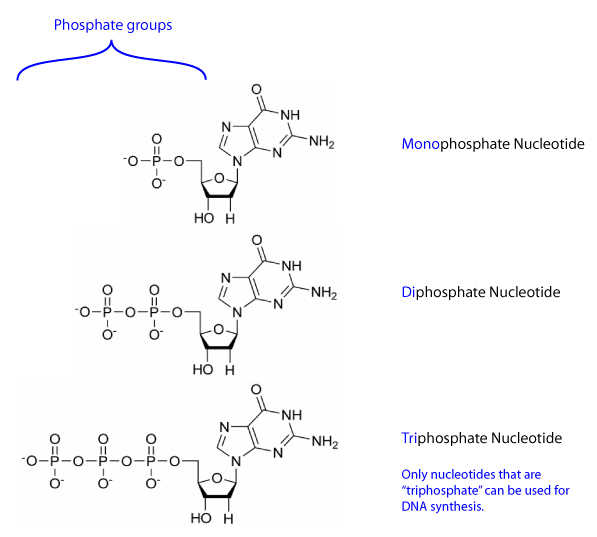 www.visionlearning.comdna phosphate nucleotide nucleotides iii visionlearning two groups synthesis replication phosphates used library biology
www.visionlearning.comdna phosphate nucleotide nucleotides iii visionlearning two groups synthesis replication phosphates used library biology
SOLVED:Suppose Two Phosphate Groups In DNA (each With A Charge Of -1
 www.numerade.comA DNA Molecule Has Many Phosphate Groups, As Shown Below What Type Of
www.numerade.comA DNA Molecule Has Many Phosphate Groups, As Shown Below What Type Of
 zuoti.proSolved:suppose two phosphate groups in dna (each with a charge of -1. A dna molecule has many phosphate groups, as shown below what type of. Dna iii
zuoti.proSolved:suppose two phosphate groups in dna (each with a charge of -1. A dna molecule has many phosphate groups, as shown below what type of. Dna iii